基于 ActionChains 类的浏览器自动化交互
浏览器自动化交互(类似 RPA 浏览器操作)
鼠标动作链
在页面上模拟一些鼠标操作,比如双击、右击、拖拽甚至按住不动等,可以通过导入
ActionChains 类实现
ActionChains 执行原理
当调用 ActionChains 的方法时,不会立即执行,而是会将所有的操作按顺序存放在一个队列里,
当你调用 perform() 方法时,队列中的时间会依次执行。
有两种写法本质是一样的,ActionChains 都会按照顺序执行所有的操作。
链式写法
menu = driver.find_element_by_css_selector(".nav")
hidden_submenu = driver.find_element_by_css_selector(".nav #submenu1")
ActionChains(driver).move_to_element(menu).click(hidden_submenu).perform()
分步写法
menu = driver.find_element_by_css_selector(".nav")
hidden_submenu = driver.find_element_by_css_selector(".nav #submenu1")
actions = ActionChains(driver)
actions.move_to_element(menu)
actions.click(hidden_submenu)
actions.perform()
ActionChains 方法列表
click(on_element=None) ——单击鼠标左键
click_and_hold(on_element=None) ——点击鼠标左键,不松开
context_click(on_element=None) ——点击鼠标右键
double_click(on_element=None) ——双击鼠标左键
drag_and_drop(source, target) ——拖拽到某个元素然后松开
drag_and_drop_by_offset(source, xoffset, yoffset) ——拖拽到某个坐标然后松开
key_down(value, element=None) ——按下某个键盘上的键
key_up(value, element=None) ——松开某个键
move_by_offset(xoffset, yoffset) ——鼠标从当前位置移动到某个坐标
move_to_element(to_element) ——鼠标移动到某个元素
move_to_element_with_offset(to_element, xoffset, yoffset) ——移动到距某个元素(左
上角坐标)多少距离的位置
perform() ——执行链中的所有动作
release(on_element=None) ——在某个元素位置松开鼠标左键
send_keys(*keys_to_send) ——发送某个键到当前焦点的元素
send_keys_to_element(element, *keys_to_send) ——发送某个键到指定元素
代码示例
1. 模拟点击
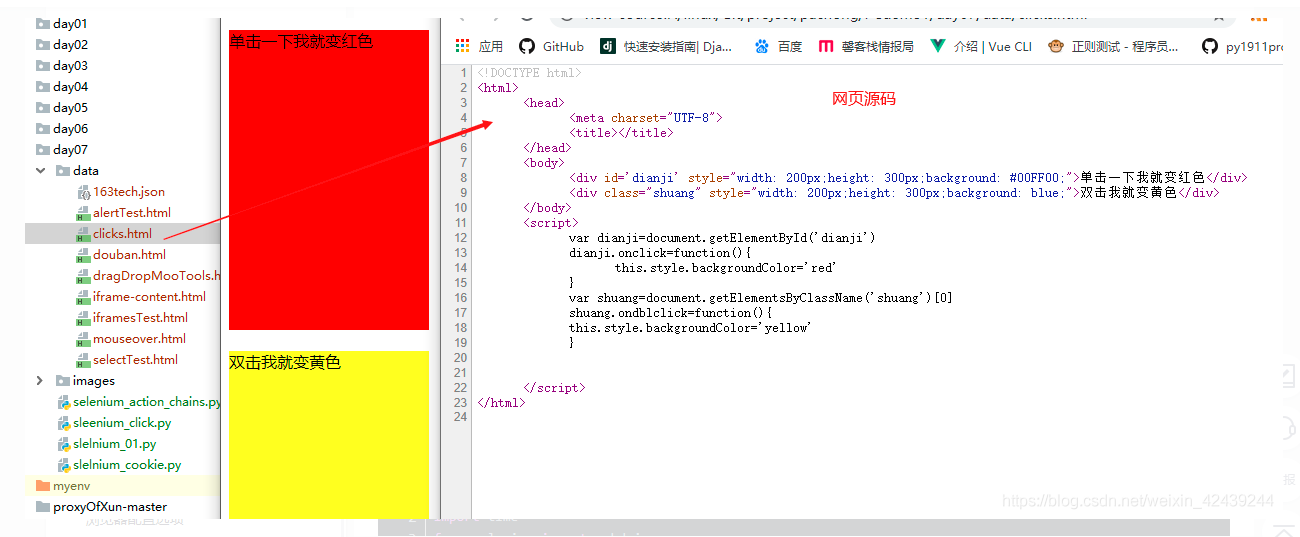
import os
import time
from selenium import webdriver
from selenium.webdriver import ActionChains
browser = webdriver.Chrome()
browser.maximize_window()
# 加载本地页面
browser.get('file:///' + os.path.abspath('./data/clicks.html'))
time.sleep(5)
click_btn = browser.find_element_by_id('dianji')
dbclick_btn = browser.find_element_by_class_name('shuang')
# 链式写法
# ActionChains(browser).click(click_btn).double_click(dbclick_btn).perform()
# 分布写法
actions = ActionChains(browser)
# actions.click(click_btn)
# 或者
click_btn.click()
time.sleep(4)
actions.double_click(dbclick_btn)
actions.perform()
time.sleep(6)
browser.close()
2. 鼠标移动
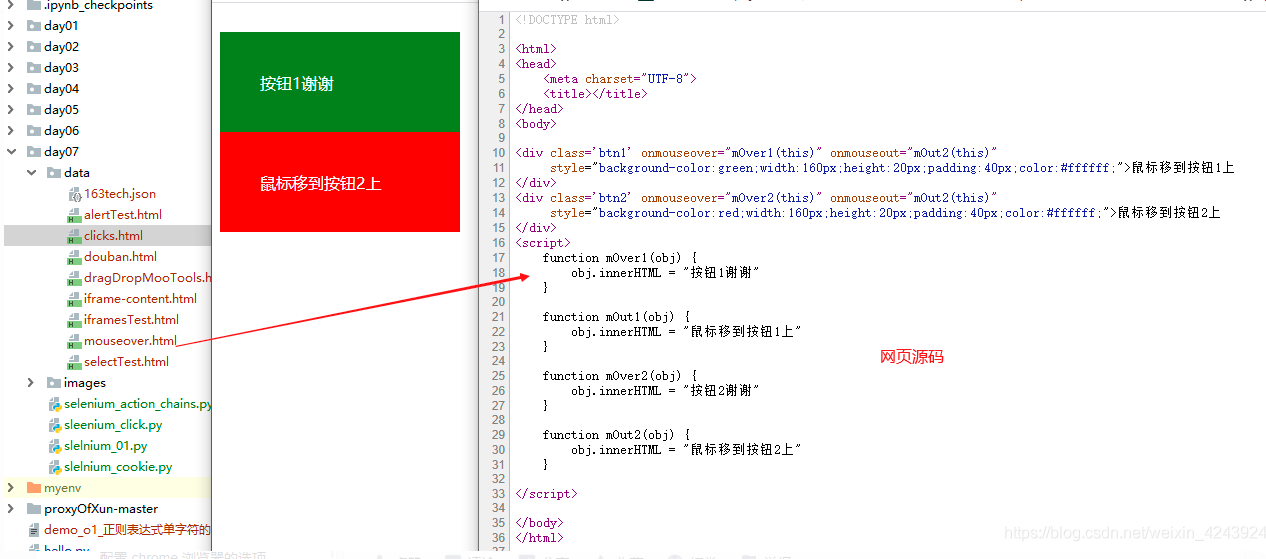
from selenium import webdriver
from selenium.webdriver.common.action_chains import ActionChains
import os
import time
browser = webdriver.Chrome()
browser.maximize_window()
browser.get('file:///' + os.path.abspath('./data/mouseover.html'))
# 定位元素
btn1 = browser.find_element_by_xpath('//div[@class="btn1"]')
btn2 = browser.find_element_by_xpath('//div[@class="btn2"]')
actions = ActionChains(browser)
# 等待
time.sleep(3)
# 移动鼠标到btn1
actions.move_to_element(btn1).perform()
print(btn1.text)
time.sleep(3)
# 生成新的actions对象
actions = ActionChains(browser)
# 鼠标移动到(10,50)也即是btn2上
actions.move_by_offset(10, 50).perform()
print(btn2.text)
time.sleep(3)
actions = ActionChains(browser)
# 从btn2移动到btn1
actions.move_to_element_with_offset(btn2, 10, -50).perform()
print(btn1.text)
time.sleep(3)
browser.close()
3. 拖拽
from selenium import webdriver
from selenium.webdriver.common.action_chains import ActionChains
from time import sleep
import os
driver = webdriver.Chrome()
driver.maximize_window()
driver.get('file:///'+os.path.abspath('./data/dragDropMooTools.html'))
item1 = driver.find_element_by_xpath('//div[@id="content"]/div[text()="1"]')
item2 = driver.find_element_by_xpath('//div[@id="content"]/div[text()="2"]')
item3 = driver.find_element_by_xpath('//div[@id="content"]/div[text()="3"]')
item4 = driver.find_element_by_xpath('//div[@id="content"]/div[text()="4"]')
item5 = driver.find_element_by_xpath('//div[@id="content"]/div[text()="5"]')
item6 = driver.find_element_by_xpath('//div[@id="content"]/div[text()="6"]')
item7 = driver.find_element_by_xpath('//div[@id="content"]/div[text()="7"]')
item8 = driver.find_element_by_xpath('//div[@id="content"]/div[text()="8"]')
item9 = driver.find_element_by_xpath('//div[@id="content"]/div[text()="9"]')
sleep(5)
action = ActionChains(driver)
action.drag_and_drop(item1, item7).perform() # 1.移动 dragger 到目标 1
sleep(5)
action = ActionChains(driver)
action.click_and_hold(item2).release(item8).perform() # 2.效果与上句相同,也能起到移动效果
sleep(5)
action = ActionChains(driver)
action.click_and_hold(item3).move_to_element(item9).release().perform() # 3.效果与上两句相同,
也能起到移动的效果
sleep(5)
action = ActionChains(driver)
action.drag_and_drop_by_offset(item4, 200, 0).perform() # 4.移动到指定坐标
sleep(5)
driver.quit()
一般用坐标定位很少,用上例中的方法 1 足够了,如果看源码,会収现方法 2 其实就是方法 1
中的 drag_and_drop() 的实现。注意:拖拽使用时注意加等待时间,有时会因为速度太快而失
败。



这里可以选择自己喜欢的 select,这里使用的 xpth 路径查找